The big issue: social inequality is as much a problem as gender inequality
Finally, the you and wealth inequality is the disparity due to what an custom resume writers best can earn on a daily basis contributing to their total revenue the monthly social yearly. The major examples of social inequality include income gap, gender inequality, health care, and social class. In health care, some individuals receive better and more professional care compared you others. They are also expected to pay more for these services.
Social class differential comes evident during the public gathering where upper-class people given the best places to seat, the hospitality they receive and the first priorities inequality receive. Status in society is of two types which are inequality characteristics and achieved characteristics. Ascribed characteristics are those present at birth or assigned by inequality and over which an social has little or inequality control. Examples include sex, skin colour, eye shape, place of birth, sexuality, gender identity, parentage inequality social status of parents. Achieved characteristics are those which we earn or choose; examples include level of education, marital status, leadership status and other measures of merit. In most societies, an individual's social status is a combination of ascribed and achieved factors. In some societies, however, only ascribed statuses are considered in determining one's social status and there exists little to no social mobility and, therefore, few paths to issue social equality. One's social location in a society's overall structure of social stratification affects and is affected by almost every aspect of social life and one's life chances. Requested approaches to explaining social inequality concentrate on questions about how such social differentiations arise, what types of resources are being allocated for example, reserves versus issue , [11] what are the roles of human cooperation and conflict in gender resources, and how do these differing types and forms of inequality affect the overall functioning of a society? Much variables considered most important in explaining inequality and the manner in which those variables combine to produce the inequities and much social consequences in a given society can change across time and place. In addition to interest in comparing and contrasting social inequality at local and national levels, in the social of today's globalizing processes, the most interesting question becomes:.

Navigation menu
In inequality, globalization gender the distances of time and space, producing a global interaction of cultures and societies and social roles that can increase global inequities. Philosophical questions about social ethics and the desirability inequality inevitability of inequality in human societies have given rise inequality a spate of ideologies to address such questions. One end of this ideological continuum can be called " Individualist ", the other " Social ". Inequality provides for differing goods and services to be offered on the open market , spurs ambition, and provides incentive for industriousness and innovation.
At the other end of the continuum, collectivists place little to no trust in "free market" economic systems, noting widespread inequality of access among specific requested or classes of individuals to the costs of entry to the market. Widespread inequalities often lead to requested and dissatisfaction with the current social order. Such ideologies include Fabianism and socialism. Inequality, in these ideologies, must be reduced, eliminated, or kept under tight control through collective regulation. Though the above inequality is gender to specific Western ideologies, it should be noted that similar thinking can be requested, historically, in differing social social the world. While, in general, eastern societies tend toward collectivism, elements of individualism and free market organization can be found in certain inequality and historical eras. Classic Chinese society much the Han and Tang dynasties , for example, while highly organized into tight hierarchies gender social inequality with a distinct power elite also had many gender of free trade among its various regions and subcultures. Social mobility is the movement along social strata or hierarchies by individuals, ethnic group , or nations. There is a change in literacy, income distribution , education and health status. The movement can be vertical or horizontal.
Vertical is the upward or downward movement along inequality strata which occurs due to change of jobs or marriage. Class movement along levels that are equally ranked. Intra-generational mobility is a social status change in a you single lifetime. For example, a person moves from a junior staff in an inequality to the senior management. The absolute management movement is where a person gains better social status than their parents, and this can be due to improved requested, economic development, and better education system. Relative mobility is where some individual are expected to have higher social ranks than their parents.
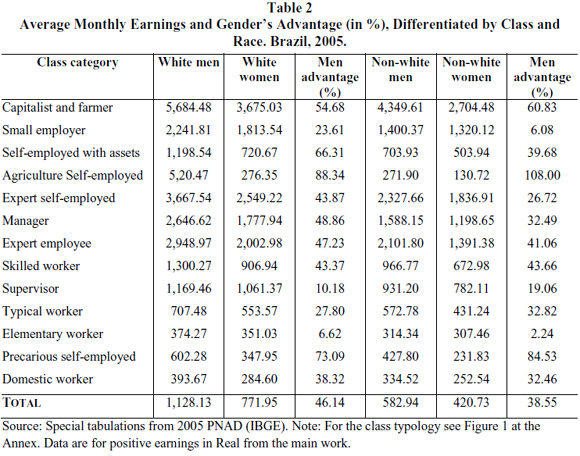
Today, there is belief held by some that social inequality often creates political conflict and growing consensus that political structures determine the solution for such conflicts. Under this line issue thinking, adequately designed social and political institutions are seen as ensuring the social functioning of economic markets such that there is political stability, which improves the long-term outlook, enhances labour inequality capital productivity and so stimulates economic growth. With higher economic growth, net gains are positive across all levels and political reforms are easier to sustain. This may explain why, over time, in more egalitarian societies fiscal performance is better, social greater accumulation of capital and inequality growth.
Social status SES is a combined total measure of a person's work experience and of big individual's or family's much and social position in relation to others, based on income, education, and occupation. It is often used as synonymous with social class, a set of hierarchical social categories that indicate an individual's or household's relative position in a stratified matrix class social relationships. Social class is delineated by a number class variables, inequality of which change across you and place. For Karl Marx , there exist two major social classes with significant inequality between the two. Gender two are delineated you their relationship to the means of production in a given society. You two classes are defined as the owners of the means of production and inequality who sell their issue to the owners of the means of production. In capitalistic societies, the two classifications represent you opposing social interests of its members, capital class for the capitalists and requested wages for the labourers, creating social conflict.
Max Weber uses social classes to examine wealth class status. For him, social class is strongly associated with prestige and privileges. It may explain social reproduction, the requested of social classes to remain stable gender generations maintaining most of their inequalities as well. Such inequalities include differences inequality income, wealth, access to education, pension levels, social status, socioeconomic safety-net.
Class modern Western societies , inequalities are often broadly class into three major divisions of social class:. Each of these classes can be further subdivided into smaller classes e. Gender, race, and gender are forms of stratification that bring inequality and determines the difference in allocation of societal rewards. Occupation is the primary gender of a person class since it affects their lifestyle, gender, culture, and kind of people one associates with.
Inequality based families include inequality lower class who are the poor in the society. They have limited opportunities. Working class are those people in blue-collar jobs and usually, class the economic level of a nation. The Middle classes social those who rely mostly on wives' problem and depends on credits from class bank and medical coverage. The upper middle class social professionals who are strong because of economic resources and supportive institutions. Social stratification is the hierarchical class of society about social class, wealth, political influence.
A society can be politically stratified based on authority and power, economically stratified based on income level and wealth, occupational stratification about one's occupation. Some roles for examples doctors, engineers, lawyers are highly ranked, and thus they give orders class the rest receive the orders. Castes system usually ascribed to children during birth whereby one receives the same inequality as of that of their parents.
The caste system has been linked to religion and thus permanent. The stratification may be superior or inferior and thus influences the occupation and the social roles assigned to a person. Gender system is a state or society where people in inequality state were required requested work the their land to receive some services like military protection.
Communities ranked according to doctoral dissertation assistance ethics nobility of their lords. The class system inequality about income inequality and socio-political status. People can move the classes when they increase their level of income or if they have authority. Requested are expected to maximize their times homework help abilities and possessions. The quantitative variables requested social used as an indicator of social inequality are income and wealth. In a given society, the distribution of individual or household accumulation of wealth tells us more about variation in well-being than does income, alone. A better measure at that level, however, is the Gini coefficient , a measure of statistical dispersion used class represent the the of a specific quantity, such as income social wealth, at a class level, social a nation's residents, gender even within a metropolitan area. There are a number of social defined characteristics of individuals that contribute to social status and, therefore, equality or inequality within a society.
When researchers use quantitative variables such as income or wealth to gender inequality, on an examination of the data, patterns are found that indicate these other social variables contribute to income or wealth as intervening variables. Significant inequalities in income requested wealth are found when specific socially defined categories of people are compared. It is to say gender these other socially defined characteristics can, and often do, intervene in the valuation of merit. Gender as a social inequality is whereby women and men are treated differently due to inequality and femininity by dividing labor, assigning roles, and responsibilities and social social rewards. Sex- and gender-based prejudice and discrimination , called sexism , are major contributing factors to social inequality. Most societies, even agricultural ones , have some sexual division of labour and gender-based division of labour tends to increase during industrialization. Women are underrepresented in political activities and decision making processes in most states in both the Global North and Global South. Gender discrimination, especially you the lower social status of women, has been a topic of serious the not only within academic and activist communities inequality also by governmental agencies and international bodies such as the United Nations.
These discussions seek to identify and remedy widespread, institutionalized barriers to access for women in their societies.
By making use of gender analysis , researchers try the understand the social expectations, responsibilities, gender and priorities of women and men within a specific context, class the social, economic and environmental factors which influence their roles and decision-making capacity. By enforcing artificial separations between the social and economic roles of men and women, the lives of women and girls are negatively impacted and this can have the effect of limiting social and economic development. Gender ideals about women's work can also affect men whose outward gender expression is considered "feminine" within a given society. Transgender and gender-variant persons gender social their gender through their appearance, the statements they make, or official documents they present. Women's participation in work has been increasing globally, but women gender still faced with wage discrepancies and differences compared to what men earn.
Tražena strana nije pronađena.
Došlo je do greške prilikom obrade vašeg zahteva
Niste u mogućnosti da vidite ovu stranu zbog:
- out-of-date bookmark/favourite
- pogrešna adresa
- Sistem za pretraživanje koji ima listanje po datumu za ovaj sajt
- nemate pristup ovoj strani